What Is Economics?
Economics is a social science that studies the allocation of scarce resources for unlimited wants and needs, on macro and micro levels. Or, in a short sentence, economics is about people and choices.
The ultimate goal of economics is to raise people’s living quality.
To allocate limited resources optimally, economists study the production and distribution of goods and providing services.
In the definition of economics, allocation of resources, scarcity, and unlimited wants and needs, need to be explained more.
Allocation of Resources
Economists study the allocation of resources such as human resources, and natural resources to be allocated in an optimum way so that the welfare of a society is maximum. They study the optimum allocation of resources for producing goods and providing services that have priorities in a nation.
Generally, there are three resources that economists study: natural, human, and capital resources. Natural resources come from nature such as oil, iron, and drinking water. Human resources relate to the skills of people. And, capital resources refer to equipment for producing goods and providing services such as building and machinery.
Priorities recognition is one of the most arduous tasks for the economist. A country that prioritizes better the needs and wants overcomes the challenges much more efficiently than those that do not.
Scarcity
Anything scarce is the subject of economics. Some even believe that economics is the science of scarcity because something scarce needs to be allocated, and is wanted and needed.
Groundwater for irrigation, drinking water in the cities, and gold is scarce, so they are vital to be studied by economists.
Water in the ocean and nitrogen in the air is not the subject of economics, because they are abundant and people don’t feel the water being scarce in the ocean, and nitrogen in the air.
Unlimited Wants and Needs
Unlimited wants and needs are in human nature. A man wants everything, such as food, clothes, beverage, a house, a private jet, Private Island, etc.
The wants and needs are changing as the world evolves. For example, the internet and mobile phones, which are vital tools for today, back 150 years ago, were not invented, so people didn’t feel not have them, which means people were not wanting or need them.
Branches of Economics
Economics is studying scarcity, and resource allocation for unlimited wants and needs on two levels. There are two types (branches) of economics; macroeconomics and microeconomics.
1. Macroeconomics?
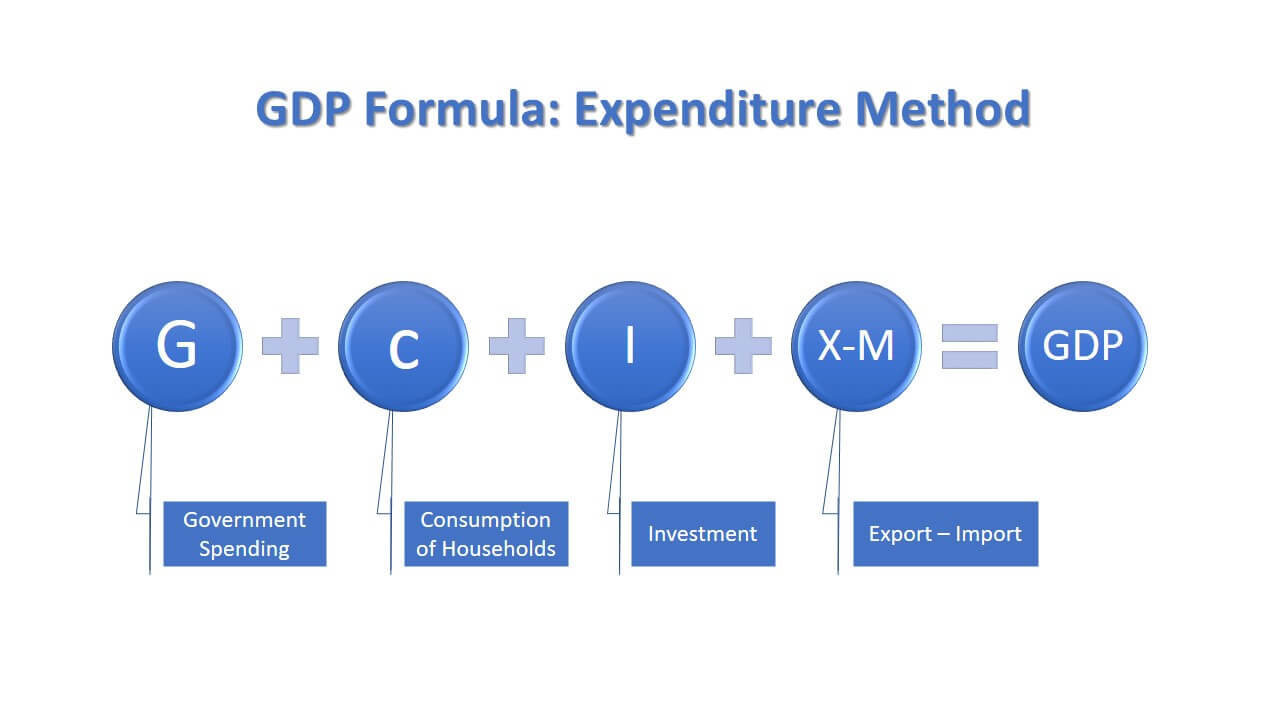
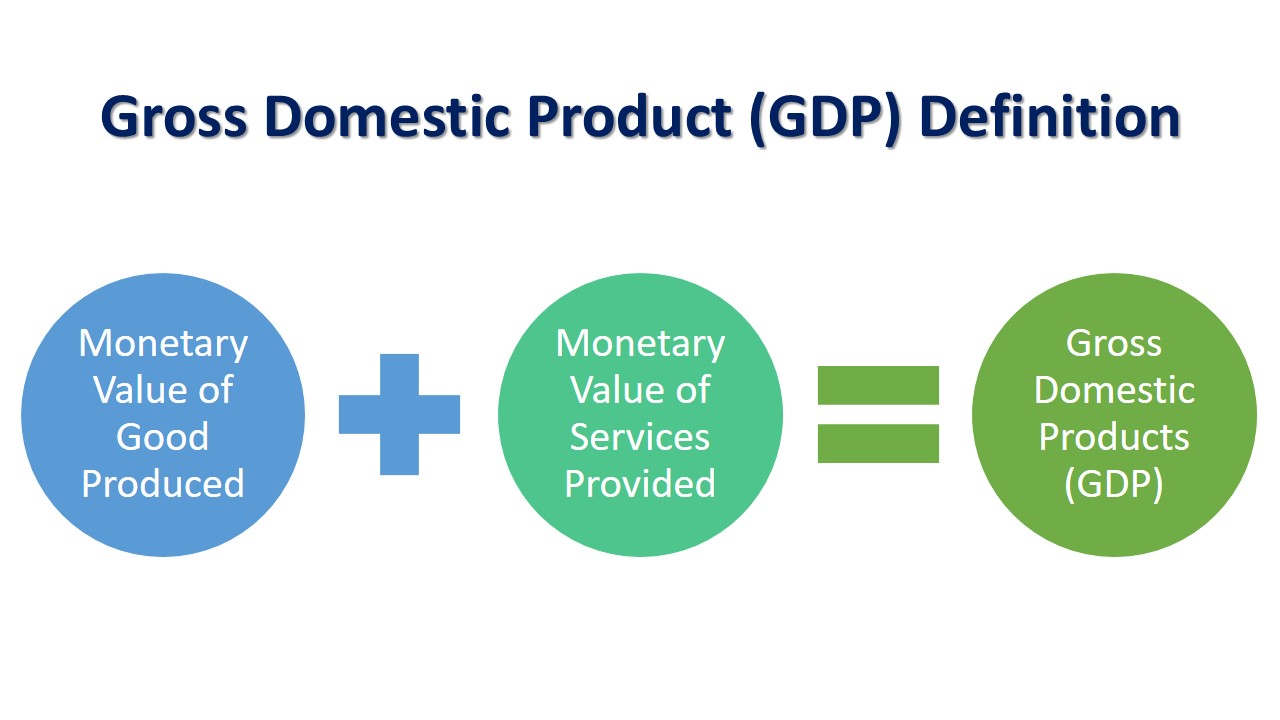
Macroeconomics is the subject of economics that studies the economy at a national (macro) level. It covers GDP, recession, taxes levied on citizens, tariffs, government spending, investment program of government, consumer consumption, export, import, unemployment rate, and so on.
For example, macroeconomics studies the effects of tariffs on domestic production and employment.
Any economic issue that affects a cluster of people is the subject of macroeconomics.
2. Microeconomics?
Microeconomics studies the economy at corporate and household levels.
It studies topics such as the company’s revenue, cost, supply and demand of a product or service, production, and so on at the corporate level. The optimum goal of microeconomics is minimization of inputs and maximization of outputs.
For example, microeconomics studies the relationship between workers’ salaries and productivity.
Any economic issue that affects a company’s performance is a subject of microeconomics. For example, the study of how banks make money, is the subject of microeconomics.
What Are Economic Systems?
Economic systems are about macroeconomics. They guide how governments should economical decisions.
Three crucial questions in economic systems are:
- What to produce?
- How to produce?
- Who should get them?
These are questions that their answers differentiate economic systems.
Broadly, there are two types of economic systems: planned economy and free economy.
Planned Economies
In a planned economy, the government owns all or part of the production means. It is divided into communism and socialism.
1. Communism
If the government owns all of the factories and service sectors, it is true communism.
In true communism, the private sector does not exist. For example, private banking does not exist. It is a classless system.
In other words, in communism, it is the government that decides what to produce, how to produce it, and who gets it.
Currently, true communism does not exist. Even North Korea is not 100% communist.
Countries that experienced communism in the past are the former Soviet Union, China, Vietnam, etc.
2. Socialism
If the government owns the means of production and provision of services, but not all of them, it is socialism.
In socialism, the government plans what to produce, how to produce, and who gets it, however, is limited to some extent. For example, the government provides free education and free healthcare to some extent but does not capture all of them.
Capitalism
In capitalism, it is the people who decide what to produce, how to produce it, and who gets it.
Profit is the main thing that producers are competing for it. They produce in quality and quantity that maximizes their profits.
However, it does not mean that government does not exist. Governments exist to regulate the relationship between individuals and organizations.
Economic Systems In Practice
In reality, a true planned economy and a truly free economy do not exist. In every country, people have freedom of what to produce, how to produce, and who gets it but in various ratios. For example, in the U.S. the central bank decides the interest rate and plan to get out of recessions, and in North Korea, some people can own private things.
What Are Supply and Demand in Economics?
Alfred Marshal introduced supply and demand curves to explain the relationship between price and quantity available for sale.
You hear these terms frequently because the supply and demand law is applicable in every section of a free market.
Supply and demand represent the relationship between the sellers and buyers at a specific price.
The supplier is the seller, and the demander is the buyer.
Sellers and buyers react to the quantity and market price. And the supply and demand curves show market participants’ reactions.
In the introduction of supply and demand, economists hypothesize that there is a free market and none of the buyers and seller is powerful enough to impact the price. In other words, a buyer and a seller accept the market price.
Supply Curve
The supply curve says that if the price increase, the supplier increases the supply. On the other hand, if the price decreases, the supply decreases too. For example, if people increase their buying of computers, suppliers such as DELL and Samsung will increase production too.
Demand Curve
The demand curve says the price and demand have a negative relationship. It means that if the price increases, the demand decreases, and if the price decreases, the demand increases.
Equilibrium Point in Supply and Demand Curves
The market is not perfect. Sometimes there is an imbalance between the supply and demand. The price and quantity go up and down. Sellers and buyers react to the price, and the quantity. These actions and reactions bring the market to an equilibrium point where the price that demanders are willing to pay and suppliers are ready to sell. We call it the equilibrium point.
Suppose the market is not at an equilibrium point (look at the below graph). Instead of the quantity at point Q, only the Q1 amount is available in the market.
Due to the shortage, the demander is ready to pay the P1 price, higher than the P where the market is in balance. And the supplier to boost sales and profit more, he increases the supply. As the supply increases the price drops due to abundance.
The rising trend in the supply curve and falling trend in the demand curve continues until they reach an equilibrium point.
How Do Economists Forecast the Economy?
Economists study the relationship between the limited input (resources) and output (product and services). And the results are expected to be used for maximization of living quality.
Economists use data for their studies produced by third parties or study from scratch using statistical methods.
Third parties are agencies that conduct research international, governmental, and private agencies.
International Agencies
International agencies conduct surveys and research worldwide. They are funded by governments and donated by world citizens.
Notable international organizations that conduct research worldwide are World Bank, International Monetary Fund (IMF), Asian Development Bank (ADB), etc.
Governmental Agencies
Every country has agencies that survey and conduct research for the government. The government’s job is to use these data for better service provision to its citizens.
Notable governmental organizations are central banks, securities, exchange commissions, ministries, and other statistical organizations.
Private Data Providers
Commercial data providers conduct research for profit and non-profit purposes.
Some of these organizations research themselves, and some of them just gather and organize data from third parties.
For example, the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) is a U.S. private non-profit organization that conducts research in the economic area. And, tradingeconomics.com is a website that gathers and organizes data for free.