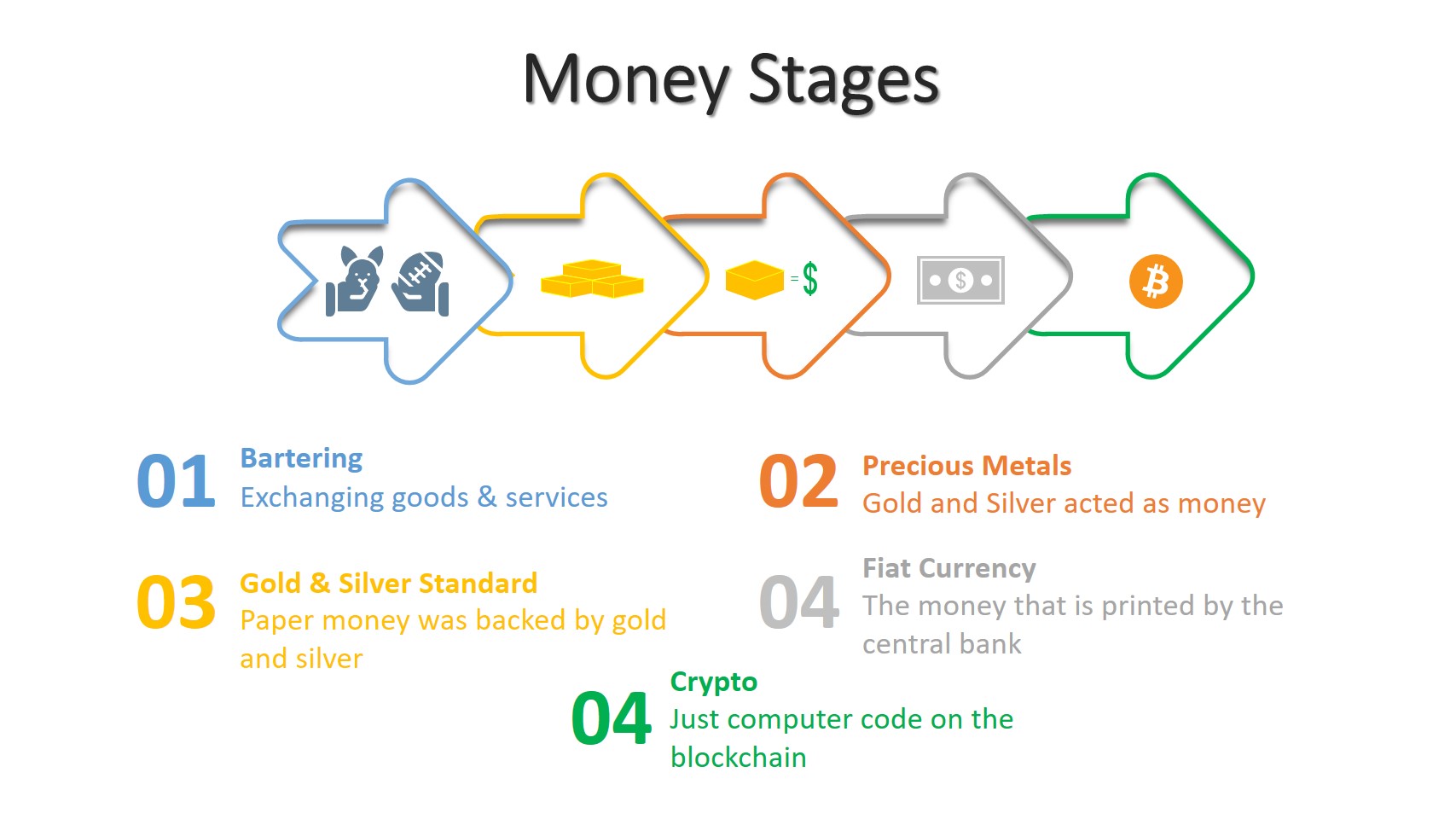
What is banking that makes bankers rich? Bankers may not be as rich as Elon Musk, but they are certainly rich.
Banking is simply channeling deposits from individuals and companies to businesses and consumers that need cash to make profits.
Suppose that Mr. Arr deposits $1m cash into BANK and the BANK lends $500k to a sugar factory and $500k to 20 families. You see that the bank channeled money from Arr to the sugar factory and 20 families.
What Is Commercial Banking?
Commercial banking is channeling money between regular people and small and medium-sized companies.
Commercial banks make money by accepting deposits as accounts from people and small and medium-sized companies at lower interest rates and give loans to businesses and consumers at higher interest rates. The difference between payment and receipt of interest rate by the bank is called the spread.
Capital One Financial Corporation is an example of a commercial bank in the USA. Click here to see the full list of commercial banks in the US.
Commercial banks are involved in two types of activities: primary and secondary.
Primary Activities
Accepting deposits as accounts and giving loans to its customers are the primary activities of a bank.
1. Banks Accept Deposits
Commercial banks accept deposits and open savings, fixed, and current accounts.
Saving Account
The saving account objective is to promote saving. The holder of a saving account receives interest. They can withdraw, but banks limit to a specific amount and number of times that a client can cash out.
Fixed Account
A fixed account holder receives higher interest than a saving account holder, but withdrawal restriction is more than a saving account. Premature withdrawal is not allowed in some banks but some banks allow it by charging interest or fee.
Current Account
The current account is not limited to several transactions. Banks charge the holder of current accounts fines and fees but do not pay interest.
2. Banks Provide Loans
Banks provide and design various types of loans with different features. In this article, I explain common types of loans.
Short-term & Long-term Loans
Short-term and long-term loans are among the main primary activities of a bank. Banks provide loans to those businesses that banks think can pay back the principal and the interest amount. A higher risk of business means a higher interest rate charged by the bank.
Cash Credit
Cash credit is a short-term financing way, mostly given to business customers rather than individuals. Usually, a bank requires its customers to put financial assets as collateral in case, the customer fails to pay them back. Using property as collateral is also common. Generally, collateralized assets are worth more than the loan.
Credit Card
Banks issue credit cards to its customer to pay for goods and services in exchange for interest. Cardholders pay the amount to the issuer plus charges based on the terms and conditions of credit card issuance. Mainly, the credit card interest rate is the highest among other types of loans.
Bank Overdraft
Bank overdraft is a short-term financing source that lets the current account holder withdraw more than his balance and allows the balance to go into the negative zone. The interest and fee are applicable. Bank overdrafts are secured (backed by collateral) or unsecured.
Discounting Bill
Discounting bill is the purchase of bill receivables by banks at a lower price than their face value.
A company may have a bill receivable but not cash. So, it sells to the bank, and the bank gives cash to the bill owner after discounting the face value.
Secondary Activities
Secondary activities are functions that a bank was not meant to do at the beginning of the banking industry. Banks added these activities later to make more profits, and some of them are:
1. Letter of Credit Issuance
A letter of credit is a confirming paper from a bank guaranteeing that a buyer will pay the seller the whole amount or remaining amount on due time. If the buyer isn’t able to pay, the bank will pay the seller.
2. Wire Transfer
Banks transfer funds internally and internationally by sending them from one account to another in the same country or abroad. A bank transfers money internationally using SWIFT, MoneyGram, WesternUnion channels, etc. Domestically, a bank transfers money directly to the receiver account or employs one of the above methods.
3. Check Collection
Most banks also collect checks on behalf of its customer and cash out on the due date.
4. Forex Trading
Forex trading is the exchange of one currency with another currency or selling one currency and buying another simultaneously. It is the biggest globally in terms of volume. Banks participate in the forex market to profit or hedge their funds to lower their risks.
5. Investment
Banks join financial markets as investors, portfolio managers, or facilitators to make profits.
6. Banks Provide Locker Facilities
Some banks provide locker facilities to its customer to keep safe precious assets, such as jewelry and documents.
What Is Investment Banking?
Investment banking is channeling funds among the government, large companies, investment funds, and high net worth people.
In other words, investment banks work with large corporations, governments, and rich people.
Some of the largest investment banks in the world are JPMorgan Chase, Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, Citigroup, UBS, and Credit Suisse.
What Are Investment Banking Functions?
Investment banks work with large sums. Managing high-worth securities and large sums of money requires complex and specialized tasks.
Here are the main tasks of investment banks.
Investment Banks Underwrite Bonds and Shares
Underwriting is a guarantee to buy unsold shares issued by corporates, and bonds issued by corporates and governments.
A government may need money to finance a public project or increase spending to cut the unemployment rate. And large corporates need funds to expand their current activities, start a new venture, or even acquire another company.
When governments and companies raise funds, they go to the investment bank to price their securities and find buyers. Then, the investment bank contacts potential buyers to sell them.
And investment banks charge commissions for selling securities and guarantee to buy the unsold amount.
Investment Banks Trade and Invest in the Financial Market
Investment banks trade securities for themselves and their clients.
An investment bank that trades on behalf of its clients charges them a commission or shares the profit. And hire professional financial analysts who are very good at trading and investment.
Investment Banks Provide Advisory Services
Advisory services of investment banks are in the investment area such as acquisition, sale of companies, merging, etc.
Investment banks provide advice in critical financial areas. And have professionals almost from any industry. That is why they can provide high-quality advice.
Investment Banks Conduct Economic Research
Investment banks hire professionals and PHDs from almost any field, such as IT, auto, economists, socialists, scientists, etc. Jobs of all professionals is to conduct research.
Investment banks conduct research to sell in the market, themselves, or clients’ orders.
Generally, research paper buyers of banks are high net worth people, hedge funds, and mutual funds.
Differences Between Commercial Banking and Investment Banking
Even though both are banks, they are different.
First, commercial banks’ clients are regular people and small companies such as local shops and schools, while investment banks’ clients are large companies such as Microsoft, Meta, hedge funds, mutual funds, and rich people such as Donald Trump.
Second, commercial banks make money by accepting deposits and giving this money as various types of loans to people and small and medium-sized companies. But, investment banks make money by charging shares and bods issuers commissions, providing advisory services, asset management, etc. Or in other words, investment banks make money working in security markets.
Third, commercial banks have more branches and customers and make less money per customer. While investment banks have fewer branches mainly in financial cities such as New York, Singapore, Tokyo, and Hong Kong, but make more money per customer.
Last but not least, investment banks are regulated by the Securities and Exchange Commission, and commercial banks are regulated by central banks, for example, the Fed in the case of the USA and RBA in Australia.
What Is a Universal Bank?
Universal banks are those banks that provide both commercial and investment bank services. And they even may provide insurance services.
These banks are also known as full-service financial institutions.