Three basic economic questions are:
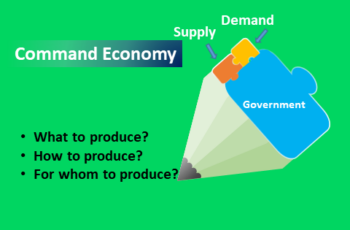
- What to produce?
- How to produce? and
- For whom to produce?
Who answers these questions?
The short answer is that the ruling economic system answers and makes economic decisions.
In the following, you will read in more detail each of these questions one by one.
What to Produce?
The first among three basic economic questions is what to produce.
According to economics, people have unlimited wants, but resources are scarce and limited.
If you are a producer and want to decide what to produce, you will produce the most profitable good. You do your research, start production, and hope to get a good result.
What about authorities?
It depends on the economic system.
In a traditional economy, elders and landlords will decide what to produce. Elders make decisions based on their experience and what they have learned from their fathers.
In a market economy market forces decide what to produce. Companies will produce profitable goods and services. They are free to decide what to produce and the law protects them.
In a command economy, it is the government decides what to produce. Residents have no role in decisions regarding what they need and want.
In a mixed economy, decisions are divided between the private and public sectors. The government decides what to produce to correct the market. And, the private sector produces what is profitable.
How to Produce?
The second question among the three basic economic questions is how to produce.
In a traditional economy, producers produce agricultural products. They use simple tools they have learned how to use from their ancestors. The way that they produce is passed down by generations with small changes.
In an open market, producers make how to produce decisions considering the available technology and cost of the labor force. Generally, in a developed nation, a manufacturer is capital-intensive, which means using more technology and machines. On the other hand, in a poor country, because labor is cheap, producers hire more workers and use fewer machines.
In a command economy, the central authority decides how to produce. Generally, decision-makers choose to use more labor than machines to bring down the unemployment rate. And residents have no choice but to accept their decisions.
In a mixed economy, both the public and private sectors answer economic questions. The private sector tends to use technology more than the public. Bureaucracy causes a delay in the adoption of new technologies by the public sector.
For Whom to Produce?
The final economic question of three basic economic questions is for whom to produce?
In a traditional economy, producers often produce for themselves and exchange the excess for other goods and services. Life is simple and free of mental stress. But, the physical body works hard and tolerates a lot.
In a free economy, the answer is simple. Anyone who pays the highest will receive. If the supply is low, a product can shoot up in price and come down at the same speed if supply increases.
In a command economy, the government decides who should get it and what people should produce. Freedom is non-existent or limited. People get what the central authority gives.
In a mixed economy, the government and the private sector make their decisions on who should get a produced product. Generally, the government produces goods that everyone needs and residents get based on laws and regulations. The private sector produces for those who pay a higher price.