Economic indicators are yardsticks that help to study past, current, and possible future macroeconomic activities.
Government agencies, international organizations (ex: World Bank and IMF), and private entities (ex: credit score agencies) collect data in the form of census or survey and organize and evaluate it to produce an economic indicator.
Government officials, producers, investors, traders, and universities use economic indicators to interpret and forecast the economy. These indicators are sources for financial analysis and evaluation of economic health.
Economic indicators are objective because they are numbers and facts collected from the real world.
As a trader or investor, you need to understand, follow and interpret them as accurately as possible. A more accurate interpretation will lead to a high-quality forecast. And accurate predictions lead to better investment and trading decisions.
Government officials, producers, investors, traders, and universities use economic indicators to interpret and forecast the economy.
As a trader or investor, you need to understand, follow and interpret them as accurately as possible. The more accurate interpretation will lead you to a more high-quality forecast and better investment and trading decisions.
Types of Economic Indicators
There are three types of economic indicators leading, coincident, and lagging.
Putting an indicator into a category is sometimes subjective. However, it is important to interpret the output data as much as possible.
A. Leading Indicators
Leading indicators predict future economic activities and trends of specific assets. These indicators are used heavily by investors and traders for forecasting future trends.
In other words, leading indicators look forward to the future.
Examples of leading indicators:
- Initial Jobless claims
- Yield curve
- Building permits
- Consumer durable Orders
- Net business formation
- Capital goods Order
- Manufacturing orders
- Stock Market Performance
- Retail Sales
- Inventory levels
- Manufacturing activities
B. Coincident Indicators
Coincident economic indicators show the current condition of the economy.
Examples of Coincident Indicators
- Employment level
- Real wages
- Retail sales
- Industrial production
- Average hours worked in manufacturing
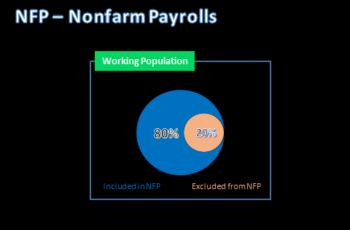
- Non-farm payroll
C. Lagging Indicators
Lagging economic indicators show the output of economic activities. They have happened in the past and might be a good or a bad sign.
Some of the lagging indicators are:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- Unemployment rate
- Consumer price index (CPI)
- Consumer confidence
- Producer price index (PPI)
- Interest rate
- Profit earned by companies
- Sales by companies
How to Find Economic Indicators?
You can find all this data on their official websites or other data providers. If you are a good reader, visiting their official websites is better because they elaborate in detail.
However, visiting every single official website is cumbersome because there are many.
The best alternative option is to track them on an economic calendar. An economic calendar is a trading tool that displays economic indicators data, reports, and speech as they are released.





Shirdagh
Good thing