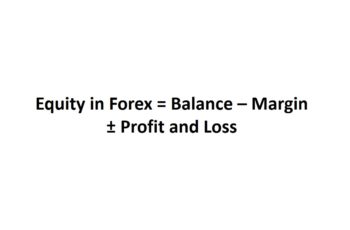Margin, Free Margin, Margin Level, Margin Call, and Stop Out can be confusing for new traders. These are crucial to understanding because they define a trader’s ability to place a trade. Additionally, forex brokers make decisions based on these factors when a trader’s account reaches some limitations.
To understand them well I have explained them in the following simple words. Keep reading!
Margin
Margin is the minimum amount of money needed to place a trade.
The required margin for a trade depends on your leverage. Higher leverage means less margin required to place a trade.
Margin Level
Margin Level represents the ratio between your equity and the margin.
Forex brokers calculate the Margin Level based on the (ML = E/M*100). Higher Margin Level means more available funds for trade, and a lower Margin Level means fewer funds available for trade.
All trading platforms calculate the margin level for you automatically based on your broker’s terms and conditions.
If you don’t have an open position, your Margin Level will be zero.
Moreover, the Margin Level depends on volume, type of market (Forex, CFD, and Stock), and Leverage. Margin Level is updated on your platform automatically.
Free Margin
Free Margin is the amount of money available for new trades. Mathematically, Free Margin = Equity – Margin.
Margin Call
Margin Call is a notification by your trading platform to make you aware that you are going out of funds.
A Margin Call is sent to you when you reach a specific Margin Level. The Margin Call level depends on your trading account type and your broker. Some brokers send you a Margin Call when your Margin Level reaches 50% and some 30%.
Stop Out
Stop Out is a level of Margin Call that your trade will be closed automatically by your broker due to insufficient funds. If you have multiple open positions, some brokers close your largest and some your first position.
Fixed and Floating Margins in Forex
Depending on your broker’s policy and account type, the margin is fixed or floating.
The fixed margin is always the same, irrespective of economic events or time during the week or day.
On the other hand, the floating margin varies when organizations release new macroeconomic events data, during specific days of the week and when your account balance changes.
How to Calculate Margin in Forex?
Often brokers have a margin requirement calculator. However, you may want to know mathematically.
Generally, you can calculate the margin requirement in the base currency of the pair or account currency.
Margin Requirement Calculation In the Base Currency
The formula of margin requirement calculation in the base currency is: (Margin Requirement = Trade Size in Base Currency / Leverage Size)
Example:
Calculate the margin requirement of 3 lots of EURUSD with a leverage of 1:50.
Solution:
Margin required = 3 * 100,000 / 50 = 6000
The above solution means that you need 6000 Euro to buy 3 lots of EURUSD.
Margin Requirement Calculation In the Account Currency
The account currency refers to the currency that a trader measures his account and profit and loss.
Generally, a trader selects his account currency when he opens an account. However, changing account currency is possible anytime that a trader wishes.
To calculate your margin requirement in the account currency, use the following formula:
Margin Requirement = (Trade Size * Exchange Rate of Base Currency to Account Currency / Leverage)
Example: Calculate margin requirement of AUDNZD of 2 lots if the account currency is USD with leverage of 50.
Solution: To solve the above problem, we need to find the exchange rate of the base currency to the account currency, or AUDUSD. Suppose that AUDUSD = 0.9000.
Margin Requirement = 200,000 * 0.9000/50 = 3,600
Based on the above example you need to have 3,600 USD to place 2 lots of AUDNZD.