What is the Money Supply?
The money supply (MS) is the total amount of currency in circulation and demand deposits at an interval of time.
What are M1, M2, and M3 Money Supply?
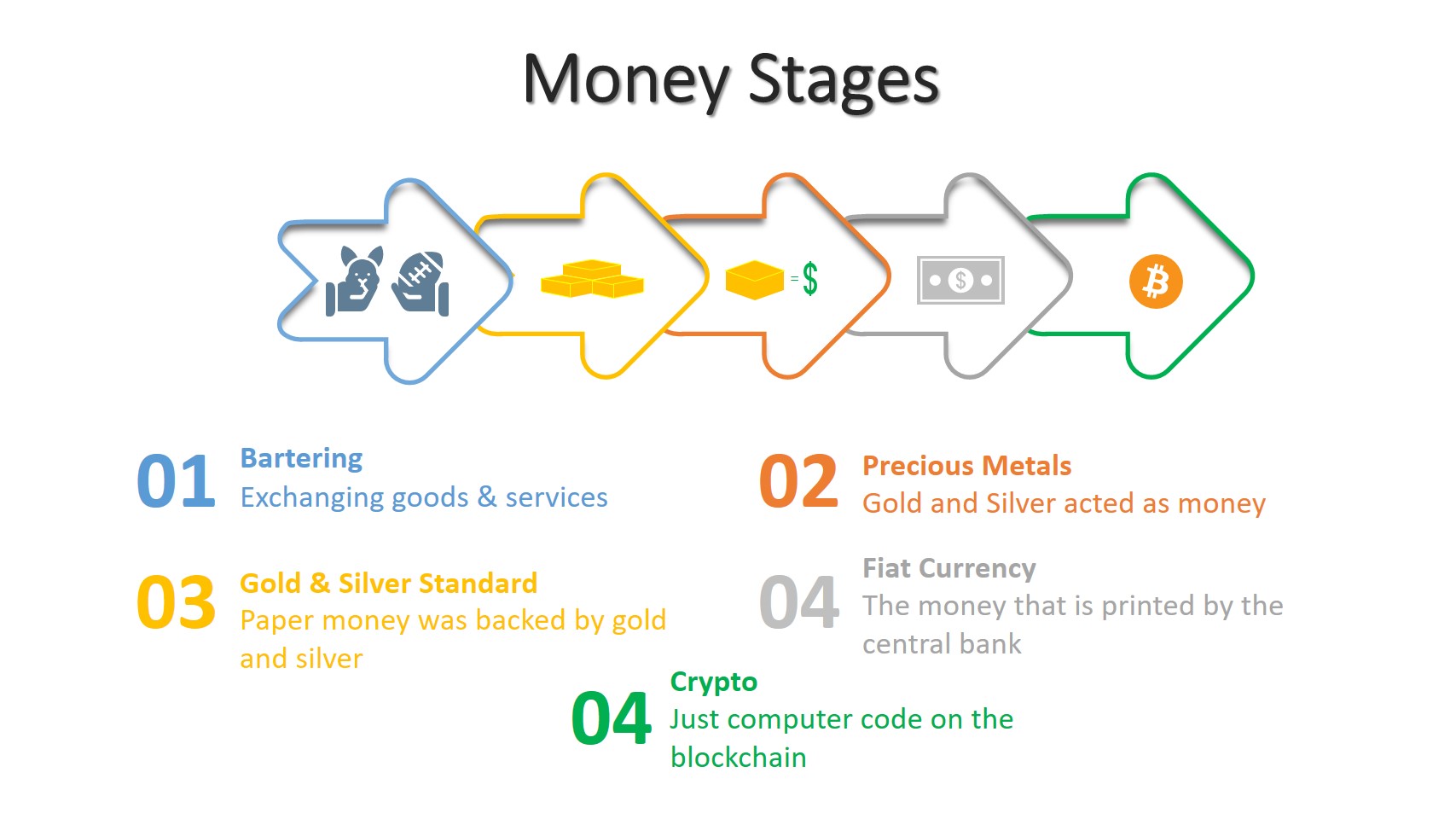
Governments classify the money supply on the scale of Ms. In the United States, they are M1, M2, and M3. In some other countries, these Ms. are M0, M1, M2, M3, and M4. The Ms starts from fastest spendable money to least spendable money.
First, let’s explain the money measurement system in the United States.
M1 includes cash and current accounts (also called check accounts), prepaid cards, deposits in digital wallets, and other types of money that are instantly available for spending.
M2 is M1 plus savings held by the public, fixed accounts in commercial banks, certificates of deposits (CDs,) and other deposit accounts of money which are usable after a few days or after being charged penalties.
M3 is M2 plus savings by large organizations like pension funds held for future spending.
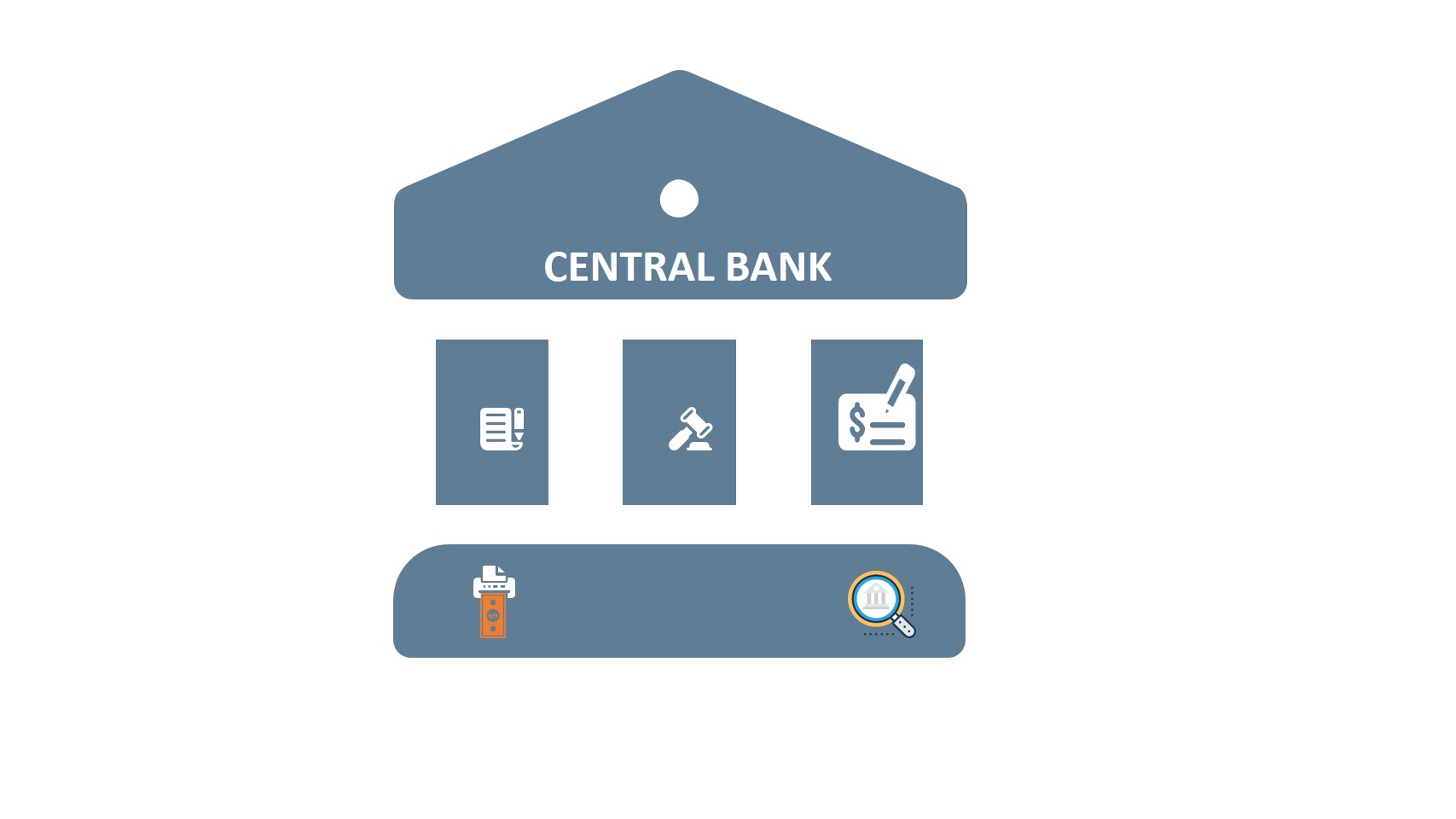
How does Central Bank Control MS in the Economy?
The money supply is controlled and regulated by central banks, for example, Federal Reserve in the United States. Central banks manage it by controlling interest rates and requiring a percentage of deposits as reserves by financial institutions, commercial banks, and other available tools. This way this entity can impact both the money supply and the money demand.
Open Market
A central bank can manipulate the amount of money in the open market by selling or buying bonds.
When a government buys bonds by paying cash, the money increases in the market, and it sells bonds by receiving cash, the opposite happens.
Interest Rates
Central banks increase the money supply by lowering interest rates to encourage investments. More investments result in more spending by corporations and creating more jobs, which results in more spending by individuals. The government cannot continue increasing the money supply because continuing the money supply cause inflation, so the government may decrease it by raising interest rates.
Required Reserve Ratio
Raising or lowering the holding reserves requirement by financial institutions, increases or decreases the amount of money in the economy. When the required holding reserves percentage is low, banks can lend more thus, creating or supplying more money. When more money supply is necessary, the central bank may raise the required reserves ratio.
Debasement
Debasement is lowering the size of coins made of precious metals. It increases the amount of money in the economy. Its process is called re-coinage, which collects old coins and re-coin by reducing their size or adding another metal with them. Debasement is necessary because the purchasing power of money during the time decrease, thus, should decrease the intrinsic value of coins in circulation.
Control of Counterfeiting
Counterfeiting is producing fake money and supplying it to society. Criminals print fake banknotes and sell them as genuine banknotes. You can counterfeit precious metals and banknotes, but not cryptocurrencies.
What is the Optimal Money Supply?
The optimal amount of money is the amount that maximizes social benefits. The economic situation, such as inflation and unemployment rate, is crucial to consider before making a decision about the amount of money in the economy. For example, if the unemployment rate is low, it is better to increase the money supply by lowering interest rates that encourage investments.