What Is Foreign Direct Investment?
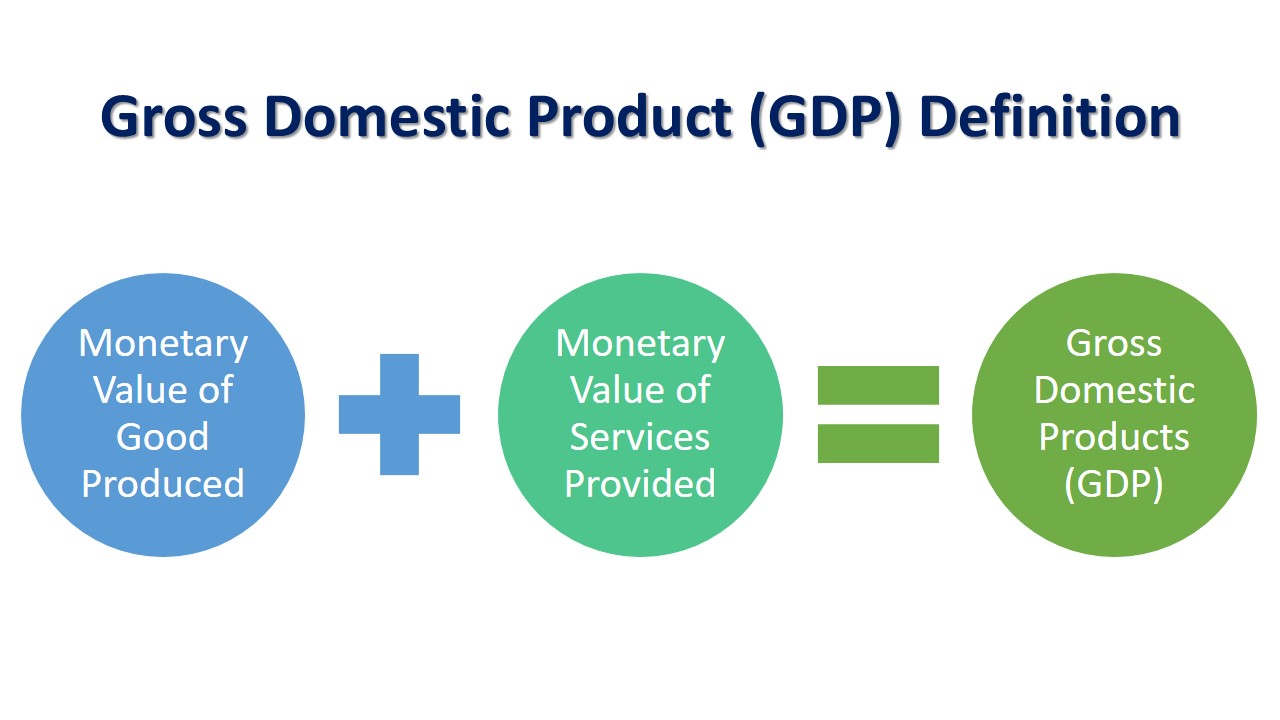
Foreign direct investment (FDI) is a long-term investment by an investor in a business in another economy that results in lasting interest with a significant influence over the overseas business. Generally, a 10% or more voting right is considered as a significant influence.
In an FDI deal, the foreign investor is called the direct investor, and the business that receives funds is a direct investment enterprise.
For example, in early 2018, the Japanese firm SoftBank bought 15% of Uber, a US company. In this case, SoftBank is the direct investor, and Uber is the direct investment enterprise.
Foreign investment and foreign direct investment can be different. In the FDI, direct investors control the management (at least 10%) of the direct investment enterprise. If control is not involved, then it is in the portfolio investment category or another category.
FDI is a significant component of the financial account of the balance of payments, others being the capital account and the current account.
Outward Foreign Direct Investments and Inward Foreign Direct Investments
Foreigners alone do not invest inside a country. Residents invest abroad too.
When foreigners invest inside a country, which is an inflow of funds, it is known as Inward FDI. Contrarily, if residents invest abroad, which is an outflow of funds, economists call it Outward FDI.
According to accounting rules, the accountant should record the inflow of funds as credits and the outflow of funds as debits.
For example, suppose an American buys 20% of a Chinese company for 20 million dollars resulting in 20% control of the company. In this transaction, the accountant records 20 million dollars as debit in the balance of payments of the USA and the same amount as credit in China’s balance of payments under the FDI account because the ownership of control exceeds 10%.
Sources provide data on FDI flows on a net basis (credits less debits). FDI net inflows are the net value of inward direct investment by foreigners including equity capital, retained earnings, and inter-company loans. Conversely, the FDI net outflows are the net value of outward direct investment made by residents including equity capital, retained earnings, and inter-company loans.
As a result, when the FDI account is negative, it indicates that investment inflows are less than outflows, and vice versa.
Types of Foreign Direct Investments
Investments flow between economies in various ways. An investor may set up completely a new business, merge with another company, or acquire another business.
1. Setting Up a Business
Setting up a business in another country is an easy way to enter a new market. It enables the company to acquire new knowledge and even access other markets through exports. For example, Tesla built a factory in Shanghai to get access to the Chinese market and export to Europe too.
2. Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers and Acquisitions happen between two businesses.
The merger means a combination of two companies into one. Two companies agree to become one to grow together. They may avoid competition or begin to compete with another bigger one. In a merger, funds may flow from one country to another. After completion of the deal operate as one company.
The acquisition means buying another company. Generally, a large company acquires a smaller company. However, there is one type of company meant to acquire another company, known as a Special Purpose Acquisition Company (SPAC). A SPAC is just a shell company to bypass the IPO process and take another bigger company to the public. A company may acquire another company to access its patents or market. It may have the will to grow fast. The reasons can be many.
Benefits of Foreign Direct Investments for Investors
Investors need to directly invest abroad to grow and cut expenses.
Motives to invest in another country could be several. Here are some of them: building a network, access to new markets, access to technology, and access to natural and human resources.
1. Building a Network
Investors if they are individuals or companies build friendships and relationships through direct investments.
Communication is a key element in a company’s success, specifically in raising funds. Investing abroad introduces investors to capital firms, politicians, and analysts.
Moreover, a network is essential for the supply chain. A company alone cannot produce and sell everything. Its products and services are a result of the communication network.
2. Access to a New Market
Companies that want to grow need to have access to new markets.
New markets or economies may have put restrictions on imported products. A country puts tariffs or restrictions on foreign goods to encourage/force producers to produce domestically.
For example, Tesla wanted to have access to the Chinese market. Exporting Tesla to China was not a competitive way. So, it built a factory in Shanghai.
3. Access to New Technologies
A company should build a new technology or get access via a deal. And direct investment in a company is an easy way to get access to its technologies.
For example, Tata bought Jaguar and Land Rover from Ford in 2008 and got access to its technologies such as the Terrain Response system.
4. Access to Cheap Natural and Human Resources
Investing abroad gives companies access to cheap human and natural resources.
Some neutral resources are difficult to ship abroad, making it important to invest in the home country. Moreover, some countries have put restrictions on exporting raw materials. For example, TotalEnergies, a French company is present in over 100 countries to access natural oil and gas.
Human resources are expensive. The difference between salaries and wages in a developed nation and a developing nation can multiple fold. So, a company may get forced to produce in cheap labor countries. For example, western clothing brands have invested in Bangladesh to produce and then sell to other nations.
Advantages of Foreign Direct Investments for Hosted Economy
The host country benefits from Foreign Direct Investment specifically, if it needs knowledge, jobs, and technology and needs to increase exports and Forex reserves.
1. FDI Creates Jobs
Investments create jobs.
A new factory in a city requires human resources to start and run operations. Sometimes hundreds or thousands of employees are necessary to run a factory.
Specifically, Foreign Direct Investment creates a lot of jobs because often foreign companies run big projects. So, it brings down the unemployment rate.
2. FDI Transfers Knowledge
FDI happens between two countries. There are how to do things that one country does better than another.
The hosted country benefits from the investor country’s experience and knowledge that accumulated over the years. The foreign investor trains and transfers knowledge to new employees who may run a domestic company later.
For example, China benefited hugely from Western companies opening operations in China. Later, Chinese citizens started running their businesses.
3. FDI Transfers Technology
A new foreign investor brings new technology, specifically from developed to developing nations.
Technology development and skills to use it takes time. The hosted country benefits from FDI if the investor brings new technology, and its citizens can learn and start later their businesses.
4. FDI Increases Forex Reserves
Central banks keep Forex reserves. When a foreign company invests directly in a country, it transfers foreign currencies and exchanges to domestic currency. Thus, increases the Forex reserves.
Forex reserves are essential for the currency value stability and the nation as a whole.
5. FDI Boosts Exports
Setting up new factories increases domestic production. Part productions are consumed domestically which compete with imported goods and part of them is exported.
Export increases transfers of Forex and boosts the current account of a nation.
Disadvantages of Foreign Direct Investments for Hosted Economy
Even though governments encourage foreign investors to invest in their countries, it does not always end well.
Here are four reasons:
1. Foreign Investors May Misuse Resources
The main job of a business is to make money. Care for workers and the environment is not a priority.
A business may even become more careless if it is operating abroad. It may not care about environmental pollution and the population at all. Specifically, if the business is operating in a poor country that is very likely to be poorly regulated, it may take advantage as much as possible without caring about the environment and workers.
2. Foreign Investors Are Dangerous to Local Businesses
Often, a foreign direct investor has more funds than locals. If the foreign investor is from a developed nation that has more money to burn and is well-equipped and experienced, can easily defeat local businesses.
Moreover, most foreign direct investors are multinational corporations and have too much power. And locals may not be able to compete at all and lose control to foreigners.
3. Jobs Created Through Foreign Direct Investment May Be for Short-term
A foreign direct investor may leave after exploitation. Its job is to profit. If it thinks that staying is not worth it, it will leave.
Additionally, foreign investors may bring employees with them instead of hiring locals.
Financial Market Reaction to Foreign Direct Investments Data
FDI is a key element in the balance of payments, specifically in developing nations. It creates stable and long-lasting relations between economies in critical areas, such as employment, currency exchange rate, and more.
So, investors in the stock and Forex markets react to new data.
Foreign Direct Investment has more impact on developing than developed nations. For example, news on FDI in Pakistan hugely affects the PKR exchange rate.
Overall, better data than expected has a positive impact on the reporting economy’s stock market and related currency. The opposite hurts the domestic currency and stock market.
Final Words
Foreign Direct Investment is an investment made by non-residents that (1) establishes long-lasting interests and (2) results in 10% control of ownership.
From a resident point of view, investments by foreigners are inward FDIs, and by residents abroad outward FDIs.
Foreign Direct Investment creates jobs, brings new technology and knowledge, boosts exports, and injects Forex.
Investors take a surplus FDI as a positive sign and negative deficit FDI data.